After a resent system crash, I had to re-install winXP (Iam still on XP - vista be damned!). And after that my system was rebooting at random - within 5 minutes of startup. I removed one of the two 2GB RAM modules and rebooted. Hollaa!!! everything ok.
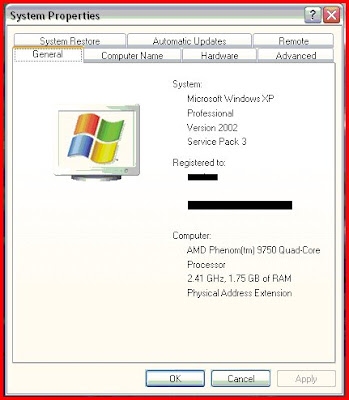
I rechecked the system configurations and found "Physical Address Extension" on system properties. I had heard about PAE before - its something to remap the memory addresses for 32-bit systems - for them, the total addressable memory is 4GB. Some part of the addressable space would be used for other hardwares. So on using 4GB RAM, only around 3GB would be available. To access the rest, PAE should be enabled (with supporting hardware).
This is what MS says about PAE:
PAE is an Intel-provided memory address extension that enables support of greater than 4 GB of physical memory for most 32-bit (IA-32) Intel Pentium Pro and later platforms.
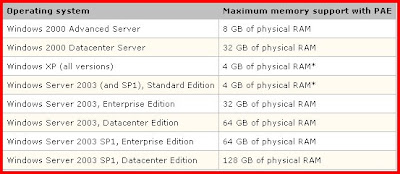
The PAE kernel is not enabled by default for systems that can support more than 4 GB of RAM.To boot the system and utilize PAE memory, the /PAE switch must be added to the corresponding entry in the Boot.ini file. If a problem should arise, Safe Mode may be used, which causes the system to boot using the normal kernel (support for only 4 GB of RAM) even if the /PAE switch is part of the Boot.ini file.
The PAE mode kernel requires an Intel Architecture processor, Pentium Pro or later, more than 4 GB of RAM, and Windows 2000, Windows XP, or Windows Server 2003.
The PAE kernel can be enabled automatically without the /PAE switch present in the boot entry if the system has DEP enabled (/NOEXECUTE switch is present) or the system processor supports hardware-enforced DEP. Presence of the /NOEXECUTEswitch on a system with a processor that supports hardware-enforced DEP implies the /PAE switch. If the system processor is capable of hardware-enforced DEP and the /NOEXECUTE switch is not present in the boot entry, Windows assumes/NOEXECUTE=optin by default and enables PAE mode.
Now I had to find out how PAE is enabled and disabled in XP - and that too was there on the same page . This is what it said:
Enabling PAE
Locate the Boot.ini file, which is typically in the root folder (for example, C:/) and remove its Read-Only and Hidden attributes.
- Locate the Boot.ini file, which is typically in the root folder (for example, C:/) and remove its Read-Only and Hidden attributes.
- Open the Boot.ini file with a text editor, and then add the /PAE parameter to the ARC path, as shown in the following example:
multi(0)disk(0)rdisk(0)partition(2) \WINNT="Windows ???? Datacenter Server" /PAE /basevideo /sos
- On the File menu, click Save.
- Restore the Read-Only attribute to the Boot.ini file.
Disabling PAE
Disable PAE by removing the /PAE parameter in the Boot.ini file. If you must disable PAE but your system processor supports hardware-enforced DEP, add /NOPAE /NOEXECUTE=alwaysoff to your Boot.ini file. Note: This will disable the DEP feature on your computer.
I changed boot.ini and rebooted the system with the whole 4GB RAM - and now everything works damn good!
0 Responses to PAE issue with AMD phenom:
Post a Comment